|
Details
Position:
Home>
Details
GH4145
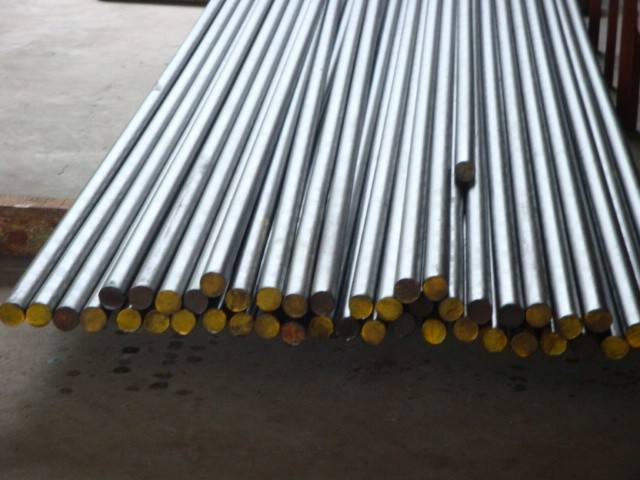
GH4145GH4145 alloy is mainly a nickel-based superalloy with γ"[Ni3(Al, Ti, Nb)] phase aging strengthening. It has good corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance below 980℃, and high strength below 800℃. It has good relaxation resistance below 540°C, as well as good formability and welding performance. The alloy is mainly used to manufacture plane springs and coil springs that require high strength and resistance to relaxation, which work under 800°C for aero engines. It can also be used to manufacture gas turbine blades and other parts. Available varieties include plates, strips, bars, forgings, ring parts, wires and pipes. Chinese name GH4145
Type alloy Material designation GH4145 (GH145)
Introduction to Alloys Material designation GH4145(GH145) Similar grades Inconel X-750 (USA), NiCr15Fe7TiAl (Germany), NC15FeTNbA (France), NCF750 (Japan) Material technical standards Q/3B 4088-1994 "GH4145 Alloy Capillary Material" Chemical composition Surface1-1
Note: Mn and Si in the table are the contents of rods, forgings, ring parts and wires. Plates, strips and pipes are: Mn≤0.35%, Si≤0.35%. Physical and chemical propertiesThermal performance It has good corrosion and oxidation resistance below 980℃, high strength below 800℃, good relaxation resistance below 540℃, and good formability and welding performance. The alloy is mainly used to manufacture plane springs and coil springs that work at below 800°C and require high strength and are resistant to relaxation. [1] Melting temperature range 1395~1425℃ Thermal conductivity Table2-1
2.1.3, GH4145 (GH145) linear expansion coefficient see table 2-2
Density ρ=8.25g/cm3 Electrical properties Resistivity at 50℃ρ=1.22*10-6Ω.m Metallographic structureThe structure of the alloy in the standard heat treatment state is composed of γ matrix, Ti (C, N), Nb (C, N), M23C6 carbide and γ'[Ni3(Al, Ti, Nb)] phase, and the γ'content is about 14.5% , Is the main strengthening phase of the alloy. Process performance requirements1. The forging temperature of the alloy is easy to form between 1220~950℃. The alloy undergoes solution treatment after the intensive forming process. Heat treatment system The solution heat treatment system for the supply of plates, strips and pipes is 980℃±15℃, air cooling. For the intermediate heat treatment system of materials and parts, the following processes can be selected for heat treatment respectively. Variety specifications and supply status We can supply various specifications of bars, forgings, ring parts, hot-rolled plates, cold-rolled plates, strips, pipes and wires. Melting and casting process The alloy adopts electric arc furnace plus vacuum consumable remelting, vacuum induction plus electroslag, electroslag plus vacuum consumable remelting or vacuum induction plus vacuum consumable remelting. Application overview and special requirements The alloy is mainly used to manufacture corrosion-resistant flat wave springs, circumferential spiral springs, spiral compression springs, spring retainers, seal rings and other parts with aero engine operating temperature below 540°C. |